News

Apr 09, 2025
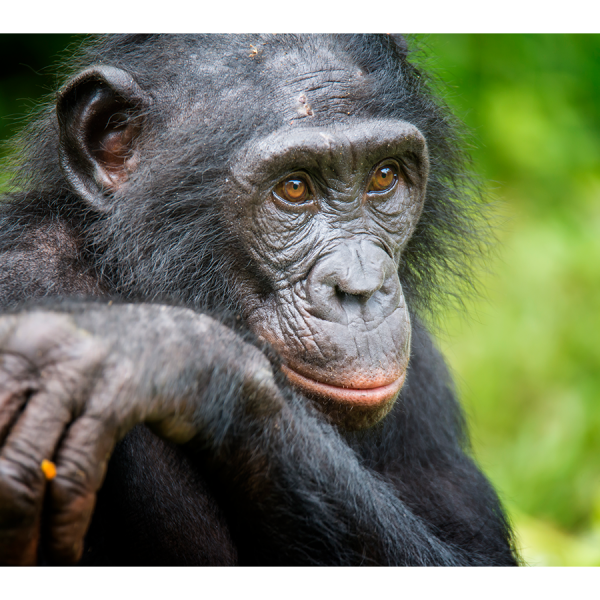
Complete genome sequences of six ape species unveiled
Previously inaccessible regions reveal novel insights that may advance understanding of evolution and conservation genetics for endangered apes as well as human health.
Full Article

Apr 09, 2025
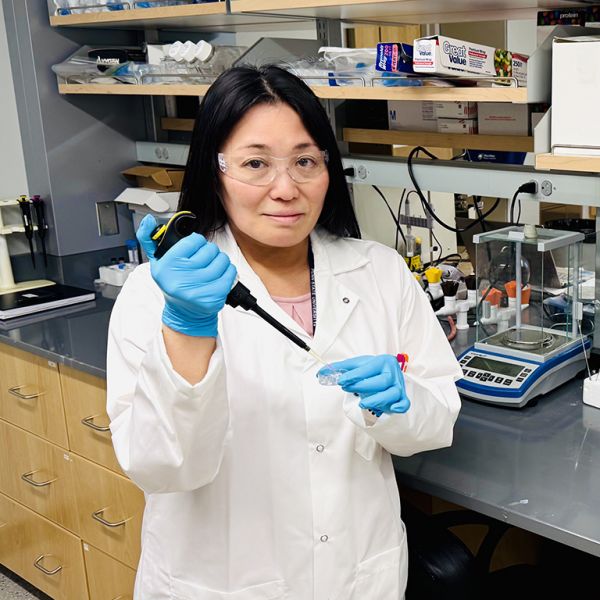
‘Patchy’ thermogels show next-gen biomedical material potential, scientists say
Special biomedical materials that can be injected as a liquid and turn into a solid inside our bodies — called thermogels — could provide a less-invasive way to deliver drugs or treat wounds. Scientists at Penn State have developed a new design for these materials that further improves their properties and may hold particular promise for use in tissue regeneration, the researchers said.
Full Article
Apr 09, 2025
NCEMS working groups to answer molecular and cellular bioscience questions
The U.S. National Science Foundation National Synthesis Center for Emergence in the Molecular and Cellular Sciences at Penn State aims to drive multidisciplinary collaboration utilizing publicly available research data.
Full Article

Apr 09, 2025
Q&A: Can artificial intelligence growth and sustainability go hand in hand?
Optimizing AI to use less energy and protect the environment
Full Article

Apr 08, 2025
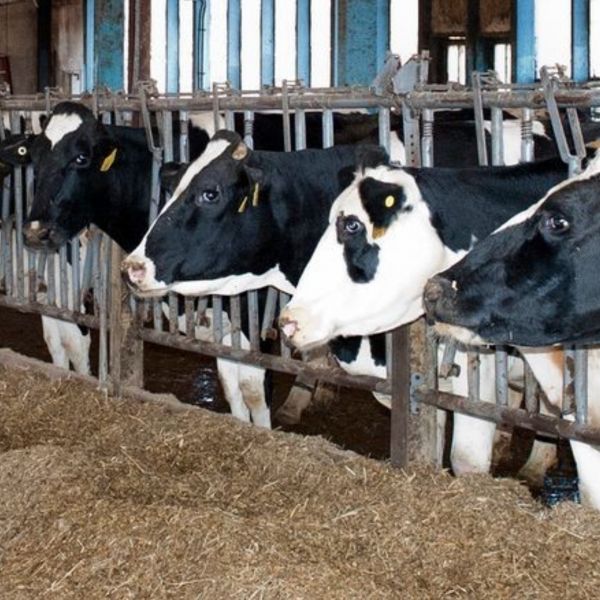
Feeding dairy cows whole cottonseed byproduct boosts milk fat, researchers find
In a new study, a team led by researchers at Penn State demonstrated that supplementing dairy cattle feed with 15% whole cottonseed can increase milk fat concentration and yield.
Full Article

Apr 04, 2025
Forty-two graduate students recognized with University awards
Annual awards celebrate graduate students' impact in research, scholarship, teaching, outreach and more.
Full Article
Apr 03, 2025
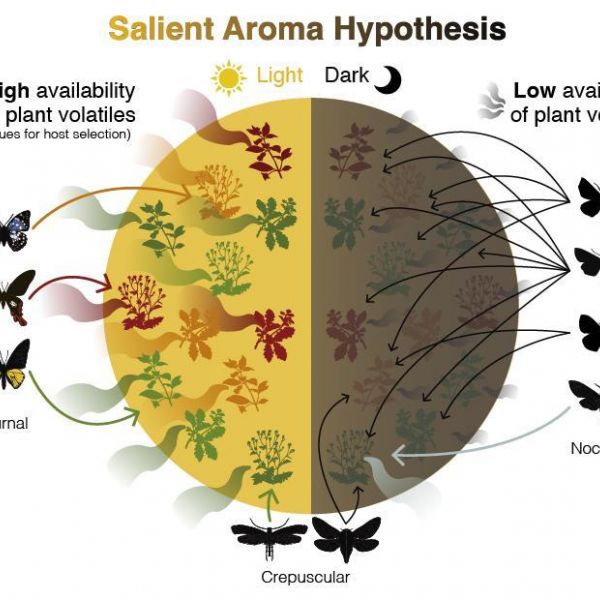
Picky eaters by day, buffet by night: Butterfly, moth diets sync to plant aromas
In a recent study published in the journal Proceedings of the Royal Society B, an international team of researchers tested a new hypothesis for why some Lepidoptera have very specific diets, feeding on only a few types of plants, while others are far less picky.
Full Article

Apr 01, 2025
Researchers working to address agricultural greenhouse gas emissions
On the latest episode of “Growing Impact,” a team of Penn State researchers discusses how their seed grant project aims to address nitrous oxide emissions from the agricultural sector by developing a system for real-time emissions monitoring and reduction.
Full Article

Mar 31, 2025
Machtinger harnesses the power of collaboration to solve complex problems
Erika Machtinger is a veterinary entomologist whose work impacts wildlife, agriculture, industry, and public health across the U.S. Her efforts hinge upon the unique, interdisciplinary ecosystem of researchers and resources at Penn State.
Full Article
Mar 31, 2025
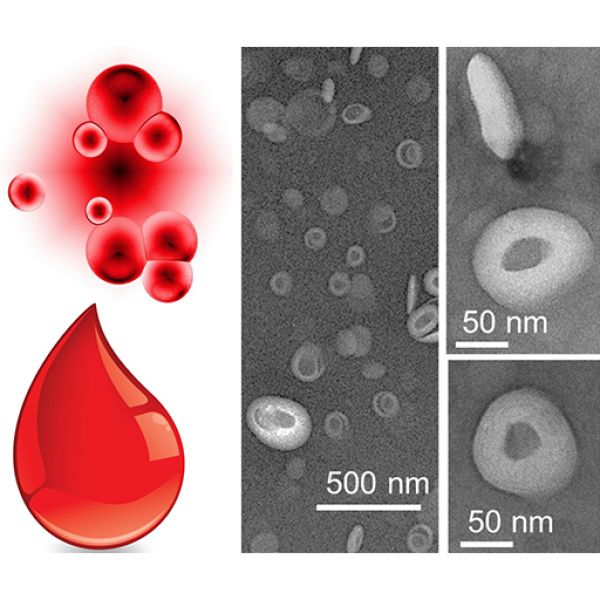
$2.7M NIH grant to fund next generation of synthetic blood
A multi-institutional team led by Dipanjan Pan, the Dorothy Foehr Huck & J. Lloyd Chair Professor in Nanomedicine at Penn State, recently received a four-year, $2.7 million grant from the National Institutes of Health’s National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute to develop the next generation of synthetic blood.
Full Article