News

Aug 16, 2022
Plant molecular geneticists discover, and begin to crack, the epigenetic code
When plants sense environmental challenges such as drought or extended periods of extreme temperatures, they instinctively reprogram their genetic material to survive and even thrive.
Full Article

Aug 16, 2022
Pulsed light technology effectively kills harmful pathogens in new study
A light-based, food sanitization technique successfully eliminated multiple harmful pathogens in a new study carried out by Penn State researchers.
Full Article

Aug 16, 2022
Researchers to develop scaffolding for nerve regeneration with $2.14M NIH grant
Peripheral nerves are responsible for moving muscles, sensing temperatures and even inhaling and exhaling; yet they comprise fragile fibers vulnerable to disease and injury.
Full Article
Aug 15, 2022
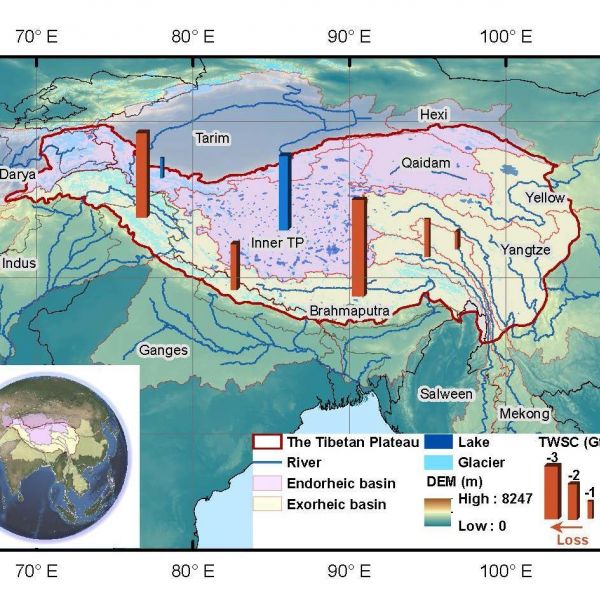
Irreversible declines in freshwater storage projected in parts of Asia by 2060
Most comprehensive study to date on water storage in Tibetan Plateau projects dramatic losses of freshwater storage in parts of Asia by mid-century under modest climate policy scenario
Full Article

Aug 11, 2022
Penn State funds study of student mental health, well-being for five more years
The coronavirus pandemic has negatively affected the mental health of college students nationwide, according to recent studies. To better serve its own students, Penn State recently funded a five-year extension of a study with researchers at the University to gain further insight into its students’ mental health status and needs.
Full Article
Aug 05, 2022
New at-home, saliva-based COVID test as effective as PCR in preliminary analysis
PCR tests, also called molecular tests or nucleic acid tests, are considered the gold standard in detecting the presence of SARS-CoV-2, the virus that gives rise to COVID-19. However, they can take a few days to process, resulting in unnecessary quarantine for negative individuals or delays for those who require proof of negative testing for travel or other commitments.
Full Article
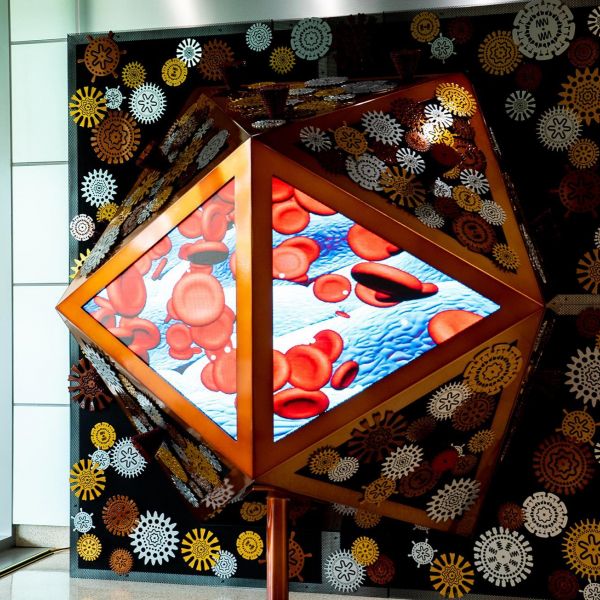

Aug 04, 2022
New SciArt installation reflects on viruses in our everyday lives
"The BioMachine," a new art installation designed and fabricated by the SciArt team at the Huck Institutes of the Life Sciences at Penn State, offers an interactive exploration of the viruses — like those which cause COVID-19 — that permeate our world.
Full Article

Aug 02, 2022
Close ties with industry fuel success for master of biotechnology degree program
Looking back over more than two decades leading Penn State’s master of biotechnology degree program, Loida Escote-Carlson concluded: “We’ve been tremendously successful.”
Full Article
Aug 01, 2022
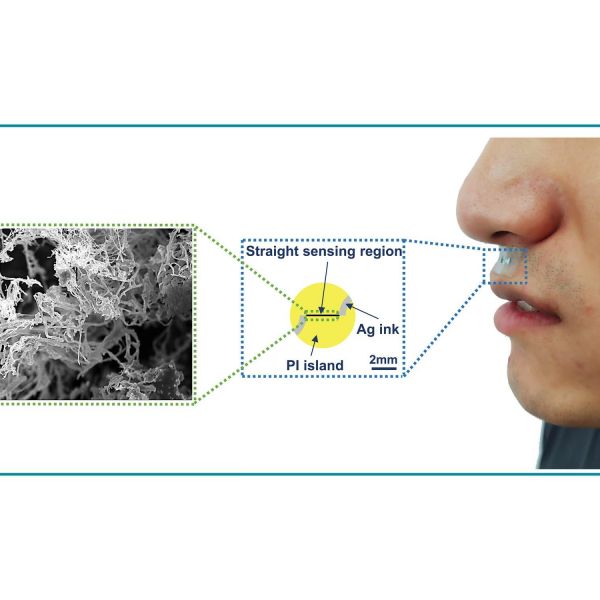
New options for health, environmental monitoring with water-resistant gas sensor
Accurate, continuous monitoring of nitrogen dioxide and other gases in humid environments is now possible, thanks to a new water-resistant gas sensor developed by Huanyu “Larry” Cheng, the James L. Henderson Jr. Memorial Associate Professor of Engineering Science and Mechanics, and his team.
Full Article

Jul 30, 2022
Undergrads to present research at public symposium on climate science, solutions
Four summer research programs that task undergraduate students with exploring pressing research related to climate science and solutions are culminating in a combined event that is open to the public.
Full Article