News

Mar 17, 2025
Ag Sciences research institute SAFES funds projects addressing critical issues
Penn State’s College of Agricultural Sciences, through its Institute for Sustainable Agricultural, Food and Environmental Science, known as SAFES, announced funding awards to accelerate the advancement of its Critical Issues Initiatives. These initiatives serve as the college’s impact hubs, addressing urgent and high-impact challenges through targeted efforts and innovative projects.
Full Article

Mar 17, 2025
Virtual lecture to explore the importance of maintaining healthy ecosystems
On March 25, Erika Ganda, an assistant professor in Penn State’s Department of Animal Science, will discuss via Zoom how microbes in animals, people and the environment are interconnected through a concept known as “One Health.” The lecture is part of the Penn State Alumni Association's Virtual Speaker Series.
Full Article

Mar 17, 2025
Graduate students to present their journeys in science
Graduate students Nazifa Tabassum and Katie Yan are this year's I AM STEM contest winners. They will serve at this year's keynote speakers for ENVISION on Saturday, March 29, where they will share their experiences in STEM and provide advice to middle school and high school students eager to get involved as scientists.
Full Article
Mar 04, 2025
Synthetic microbiome therapy suppresses bacterial infection without antibiotics
Precise, targeted treatment using limited strains of gut bacteria effectively protected against C. difficile infection, severe symptoms and recurrent infections in mice.
Full Article

Mar 03, 2025
'Growing Impact' discusses environmental contaminants, human health
The latest episode of Growing Impact discusses how environmental contaminants affect human health, a research focus for Penn State professors Andrew Patterson and Costas Maranas.
Full Article

Feb 28, 2025
New computer vision system can guide specialty crops monitoring
The technology applies an internet of things and artificial intelligence to enhance controlled environment agriculture in advanced greenhouse scenario.
Full Article

Feb 28, 2025
Penn State Ag student Auja Bywater wins global research award
Auja Bywater, a doctoral student in Penn State’s College of Agricultural Sciences, has been awarded second prize in the Global Challenges University Alliance (GCUA) 2030 research competition for her work titled “Improving Food Safety in Controlled Environment Agriculture Systems.”
Full Article
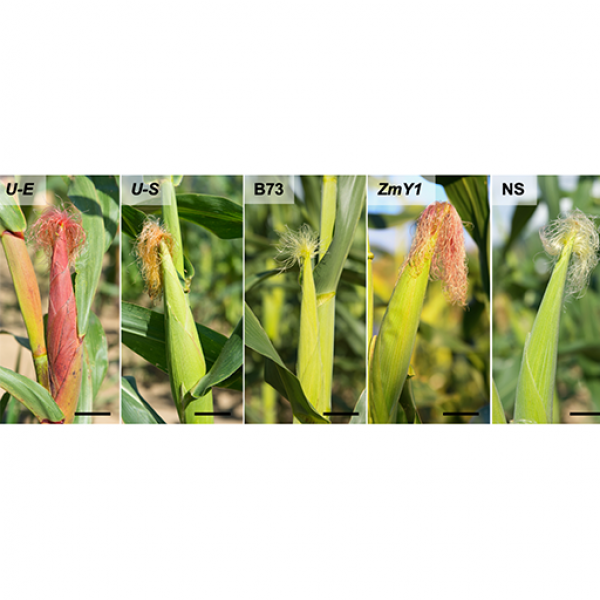

Feb 20, 2025
Select corn lines contain compounds that sicken, kill major crop pest
The compounds, called flavonoids, have an insecticidal effect on corn earworm larvae.
Full Article

Feb 19, 2025
Feb. 24 EarthTalks: Cross-disciplinary collaboration employing stakeholder input
Camelia Kantor, associate director of strategic initiatives at the Huck Institutes of the Life Sciences and associate research professor at Penn State, will give the talk, “Bridging Worlds: How Geography and Nematology Research Converge Through Stakeholder Input,” at 4 p.m. on Monday, Feb. 24, in 112 Walker Building at Penn State University Park. Talk will also be available via Zoom.
Full Article

Feb 11, 2025
Sustainable Labs Program increases participant engagement, welcomes new labs
Two upcoming virtual sessions will cover how labs can learn more and join next year’s cohort.
Full Article