News

Jul 07, 2025
‘Scialog’ grant to study how rising ocean temperatures affect fish behavior
A wildlife behavioral ecologist at Penn State is part of a multi-institution team that received funding from Scialog: Neurobiology and Changing Ecosystems, a international three-year initiative that aims to spark new science exploring neurobiological responses to rapidly changing environments.
Full Article

Jul 02, 2025
What a bumble bee chooses to eat may not match ideal diet
A new study led by researchers at Penn State suggests that what bumble bees choose to eat may not line up with their ideal nutritional needs.
Full Article

Jun 25, 2025
Warmer spots within fields have more blooms and more bees
Climate can vary across large areas of land, but it also can vary within much smaller areas such as farms. A new study by researchers at Penn State examined whether these microclimates — the climate of a very small or restricted area — affect pollination by both wild and managed bees and resulting wild blueberry yields.
Full Article

Jun 20, 2025
How a genetic tug-of-war decides the fate of a honey bee
Despite having identical genetic instructions, female honey bee larvae can develop into either long-lived reproductive queens or short-lived sterile workers who help rear their sisters rather than laying their own eggs. Now, an interdisciplinary team led by researchers at Penn State has uncovered the molecular mechanisms that control how the conflict between genes inherited from the father and the mother determine the larva’s fate.
Full Article
May 20, 2025
Urban heat portal aims to tackle rising temperatures, protect at-risk residents
As heat and associated risks intensify in cities around the world, a new tool developed by researchers in the College of Arts and Architecture’s Stuckeman School at Penn State and the Department of Urban Policy at Hunter College aims to shed light on how rising temperatures affect New York City’s neighborhoods — and what can be done to protect the most vulnerable communities.
Full Article

May 08, 2025
Some water conservation programs may get more value by targeting rural farms
Conservation programs aimed at boosting environmentally friendly practices by incentivizing farmers may get more bang for their buck by targeting rural farms rather than more urban ones, according to a study led by researchers at Penn State.
Full Article

May 08, 2025
Biological physicist Réka Albert elected to National Academy of Sciences
Réka Albert, Evan Pugh University Professor and professor of physics and biology at Penn State, has been elected to the National Academy of Sciences.
Full Article

Apr 29, 2025
Heather Hines named interim director of the Center for Pollinator Research and the Insect Biodiversity Center
Heather Hines, Associate Professor of Biology and Entomology, has been named Interim Director of the Center for Pollinator Research (CPR) and the Insect Biodiversity Center (IBC). Hines is succeeding Christina Grozinger, Publius Vergilius Maro Professor of Entomology and director of the Huck Institutes of the Life Sciences.
Full Article

Apr 24, 2025
Grozinger appointed to National Academies committee on insect declines
The National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine recently appointed Christina Grozinger, Publius Vergilius Maro Professor of Entomology and director of the Huck Institutes of the Life Sciences at Penn State, to an 18-member study committee to examine the status of insects in North America.
Full Article

Apr 16, 2025
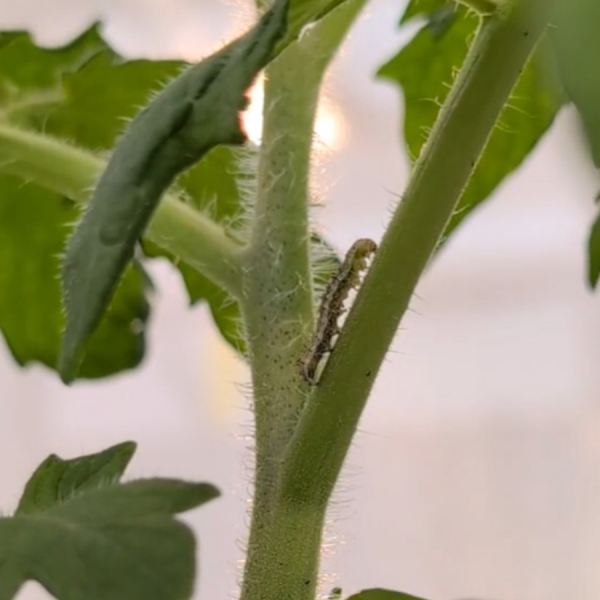
Feeling salty? Increased salt stress reduces tomato pest activity
Increased soil salinity can reduce damage from prominent tomato pests such as the tomato fruitworm, according to researchers at Penn State. They published their findings in the Journal of Plant, Cell and Environment.
Full Article