News

Mar 30, 2021
Penn State virologist Szpara to co-host COVID-19 vaccine education town halls
Moriah Szpara, associate professor of biology and of biochemistry and molecular biology at Penn State, will co-host two COVID-19 vaccine education town halls at 7 p.m. EST on Wednesday, March 31, and Wednesday, April 7, with Benhur Lee of the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai.
Full Article

Mar 18, 2021
Ottar Bjørnstad elected to Norwegian Academy of Sciences and Letters
Ottar N. Bjørnstad, distinguished professor of entomology and biology and J. Lloyd & Dorothy Foehr Huck Chair of Epidemiology at Penn State, has been elected to the Norwegian Academy of Sciences and Letters. Bjørnstad was recommended as a result of his significant contributions to the fields of population ecology and quantitative epidemiology.
Full Article

Mar 30, 2021
Tool can provide swine producers with early diagnosis of often-fatal 'Strep zoo'
A team led by researchers in Penn State's College of Agricultural Sciences has developed a diagnostic test that can identify virulent forms of the swine bacterial pathogen Streptococcus equi subspecies zooepidemicus — often referred to as "Strep zoo" — which can cause severe illness and death in pigs, other animals and rarely people.
Full Article

Mar 17, 2021
Matt Ferrari named director of Center for Infectious Disease Dynamics
Matt Ferrari, who was closely involved with multiple aspects of University and community efforts to address COVID-19, has been tapped as the new head of CIDD.
Full Article

Mar 15, 2021
Lab Bench to Commercialization grant recipients announced
Two faculty members have been selected to receive Lab Bench to Commercialization (LB2C) grants from the Eberly College of Science in 2021. The competitive program provides funding for researchers in the college, enabling them to enhance the commercial potential of ongoing research and prepare them to translate their intellectual property to the marketplace.
Full Article

Mar 10, 2021
Another common cold virus?
If it becomes endemic — circulating in the general population — and most people are exposed in childhood, SARS-CoV-2 may join the ranks of mild cold-causing coronaviruses that currently circulate in humans.
Full Article
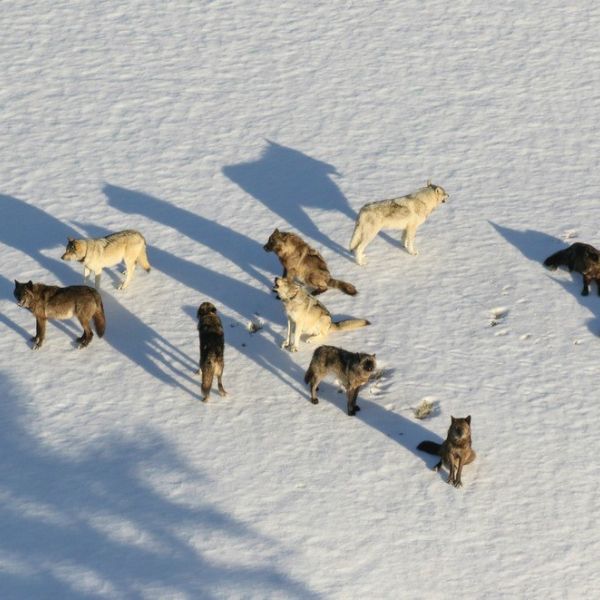

Mar 03, 2021
Wolf social group dynamics matter for infectious disease spread, models suggest
By modeling wolves in Yellowstone National Park, researchers have discovered that how a population is organized into social groups affects the spread of infectious diseases within the population. The findings may be applicable to any social species and could be useful in the protection of endangered species that suffer from disease outbreaks.
Full Article

Feb 26, 2021
Elizabeth McGraw named head of Department of Biology
Elizabeth McGraw, professor and Huck Scholar in Entomology and director of the Center for Infectious Disease Dynamics (CIDD) at Penn State, has been named the new head of the Department of Biology.
Full Article
Feb 26, 2021
Study finds short window for donating convalescent plasma to COVID-19 patients
The optimal timeframe for donating convalescent plasma for use in COVID-19 immunotherapy, which was given emergency-use authorization by the Food and Drug Administration in August 2020, is within 60 days of the onset of symptoms, according to a new Penn State-led study.
Full Article
Feb 26, 2021
Mortality rises among public when health workers get sick in an outbreak
When healthcare workers become ill during a disease outbreak, overall case counts and mortality rates may significantly increase, according to a new model created by researchers at Penn State. The findings may help to improve interventions that aim to mitigate the effects of outbreaks such as COVID-19.
Full Article