News

Mar 17, 2025
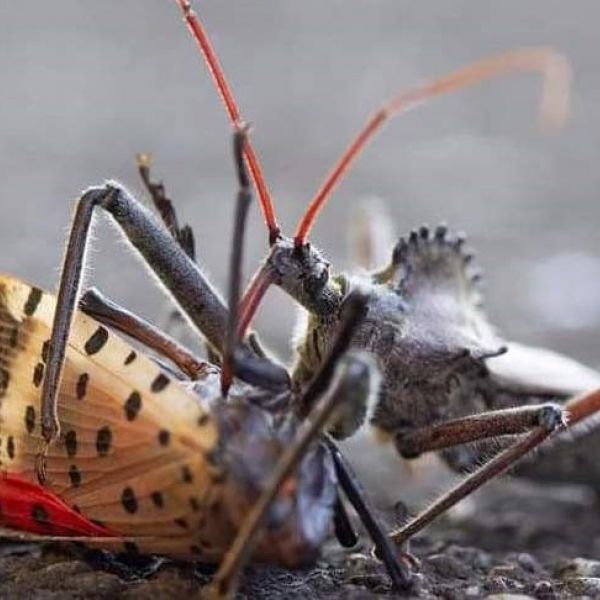
Natural insect predators may serve as allies in spotted lanternfly battle
Insect predators found in the United States could help keep spotted lanternfly populations in check while potentially reducing reliance on chemical control methods, according to a new study conducted by researchers at Penn State.
Full Article

Mar 17, 2025
Stage set for final round of Three Minute Thesis competition on March 29
Graduate students at Penn State will put their communication skills to the test in the final round of the University’s second annual Three Minute Thesis (3MT) competition. The event, hosted by the J. Jeffrey and Ann Marie Fox Graduate School, is set for 3 p.m. on Saturday, March 29, and will be livestreamed from the Nittany Lion Inn. The competition is free and open to the public, but advance registration is required for both in-person and virtual attendance.
Full Article

Mar 17, 2025
Ag Sciences research institute SAFES funds projects addressing critical issues
Penn State’s College of Agricultural Sciences, through its Institute for Sustainable Agricultural, Food and Environmental Science, known as SAFES, announced funding awards to accelerate the advancement of its Critical Issues Initiatives. These initiatives serve as the college’s impact hubs, addressing urgent and high-impact challenges through targeted efforts and innovative projects.
Full Article

Mar 17, 2025
Virtual lecture to explore the importance of maintaining healthy ecosystems
On March 25, Erika Ganda, an assistant professor in Penn State’s Department of Animal Science, will discuss via Zoom how microbes in animals, people and the environment are interconnected through a concept known as “One Health.” The lecture is part of the Penn State Alumni Association's Virtual Speaker Series.
Full Article
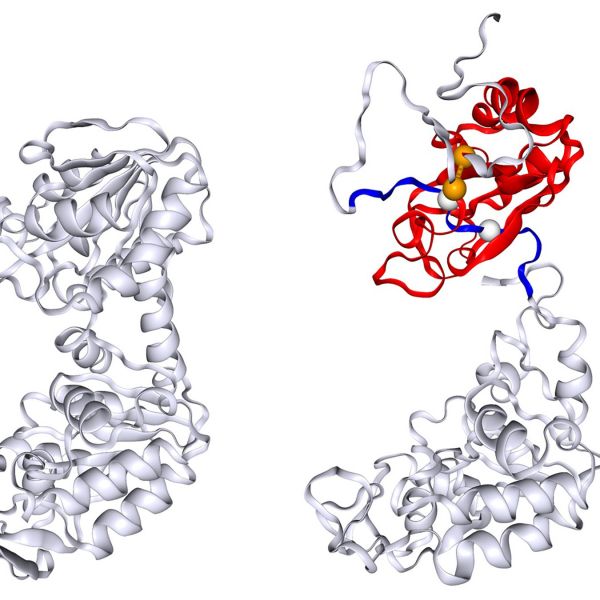
Mar 17, 2025
Protein accidentally lassos itself, helping explain unusual refolding behavior
New study demonstrates a potential protein misfolding mechanism that could solve a decades-old mystery of why some proteins refold in a different pattern than expected.
Full Article
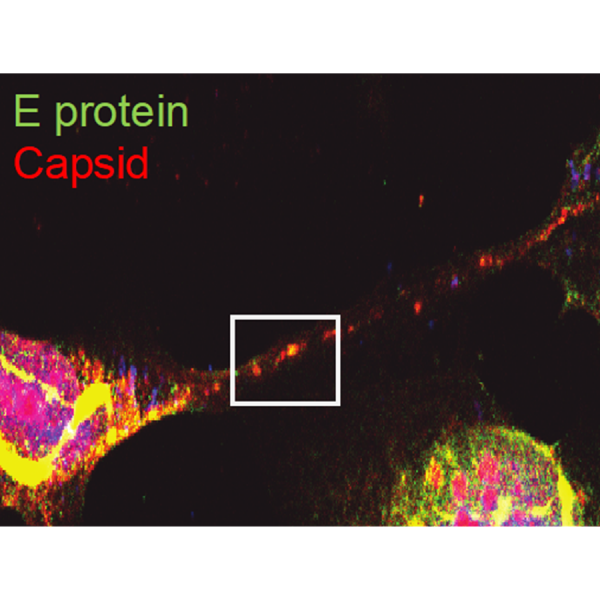
Mar 17, 2025
Tunnel-building virus: How Zika transmits from mother to fetus
A team of researchers from Penn State and Baylor College of Medicine found that the Zika virus builds tiny tunnels, called tunneling nanotubes, to stealthily transport material needed to infect nearby cells, including in placental cells.
Full Article

Mar 17, 2025
Graduate students to present their journeys in science
Graduate students Nazifa Tabassum and Katie Yan are this year's I AM STEM contest winners. They will serve at this year's keynote speakers for ENVISION on Saturday, March 29, where they will share their experiences in STEM and provide advice to middle school and high school students eager to get involved as scientists.
Full Article

Mar 14, 2025
Plant biologist awarded the Masatoshi Nei Innovation Prize in Biology
Sarah Assmann, Waller Professor of Plant Biology at Penn State, has been awarded the Masatoshi Nei Innovation Prize in Biology. The award was established through a generous gift from Masatoshi Nei, professor emeritus of biology at Penn State; Laura Carnell, professor of biology at Temple University; and Nei’s wife, Nobuko Nei. The prize is intended to recognize a preeminent scientist who is on the faculty at Penn State, is an innovator in their field, and has achieved outstanding scientific research and leadership in the biological sciences.
Full Article

Mar 12, 2025
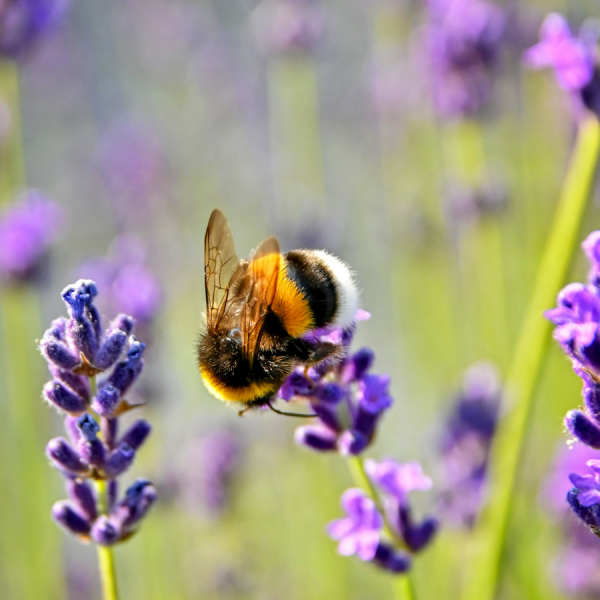
Analyzing genetic ‘signatures’ may give insight into what stresses wild bees
A new method of examining gene expression patterns called landscape transcriptomics may help pinpoint what causes bumble bees stress and could eventually give insight into why bee populations are declining overall.
Full Article
Mar 04, 2025
Synthetic microbiome therapy suppresses bacterial infection without antibiotics
Precise, targeted treatment using limited strains of gut bacteria effectively protected against C. difficile infection, severe symptoms and recurrent infections in mice.
Full Article