News

Jul 14, 2025
The breadth of the brain
Researchers in the Penn State Neuroscience Institute study the brain’s many aspects in a variety of ways, with implications from mental health to aging and disease.
Full Article
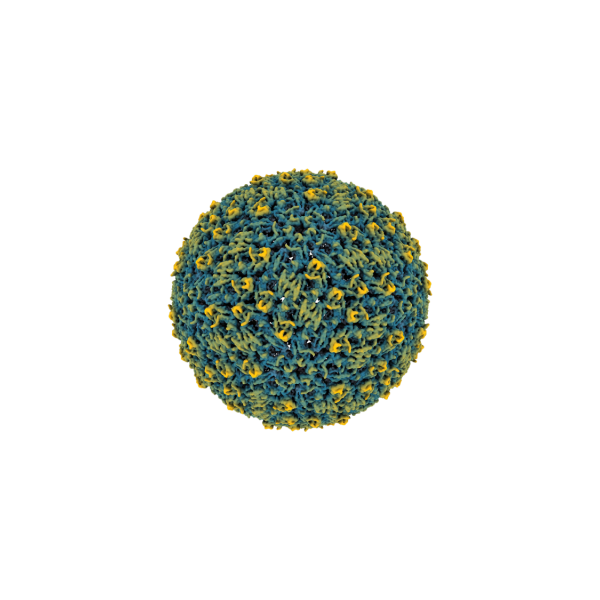
Jul 10, 2025
Structure of tick-borne virus revealed at atomic resolution for the first time
Rates of the Powassan virus infections — which can cause seizures and paralysis — are increasing across commonwealth, nation.
Full Article

Jul 07, 2025
Nighttime pistachio snacking may reshape gut microbiome in prediabetic adults
Eating pistachios every night for 12 weeks altered bacteria in the gut, according to new study.
Full Article

Jul 07, 2025
Four selected for inaugural Next-Gen Innovators Fellowship at Penn State
Four emerging leaders in science and innovation have been selected as the inaugural fellows in Penn State’s Next-Gen Innovators Fellowship program, an initiative designed to close critical training gaps in research translation and technology commercialization.
Full Article
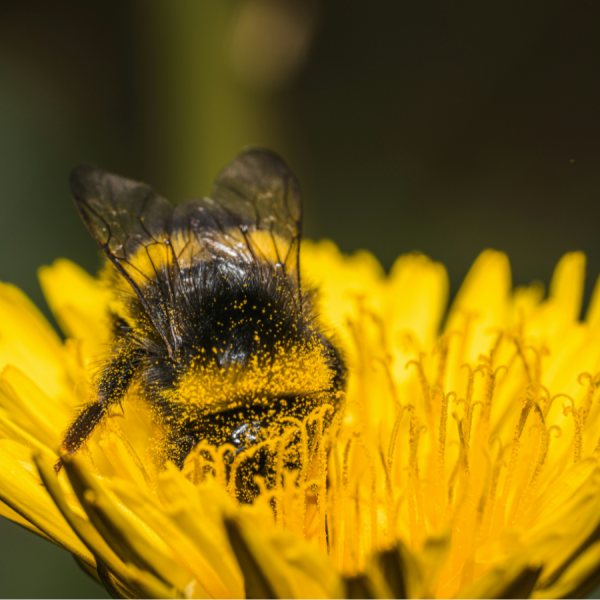

Jul 02, 2025
What a bumble bee chooses to eat may not match ideal diet
A new study led by researchers at Penn State suggests that what bumble bees choose to eat may not line up with their ideal nutritional needs.
Full Article

Jul 01, 2025
ARISE program provides hands-on training to aspiring anthropologists
A talented group of aspiring anthropologists recently traveled to Penn State to take part in the Department of Anthropology’s annual ARISE program.
Full Article

Jul 01, 2025
Lab Bench to Commercialization program broadens its scope
Eberly College of Science seed grant program to shift emphasis to earlier development of research, focusing on societal impact and career readiness.
Full Article

Jun 25, 2025
Nutritional sciences faculty receive national recognition for research
Three Penn State Department of Nutritional Sciences faculty members were recently recognized for their research contributions to the field with prestigious awards by the American Society for Nutrition (ASN).
Full Article
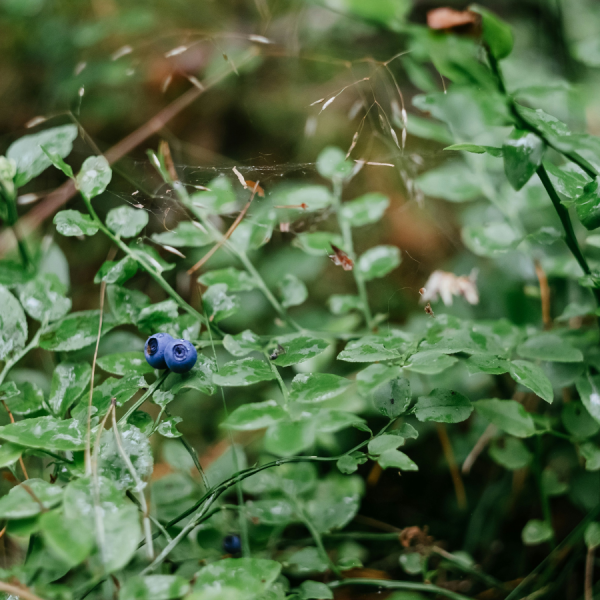

Jun 25, 2025
Warmer spots within fields have more blooms and more bees
Climate can vary across large areas of land, but it also can vary within much smaller areas such as farms. A new study by researchers at Penn State examined whether these microclimates — the climate of a very small or restricted area — affect pollination by both wild and managed bees and resulting wild blueberry yields.
Full Article

Jun 30, 2025
Huck announces 2025-26 Leadership Fellows
Three faculty members, representing three different Penn State colleges, have been named Huck Leadership Fellows for the 2025-26 academic year.
Full Article