News

Sep 21, 2023
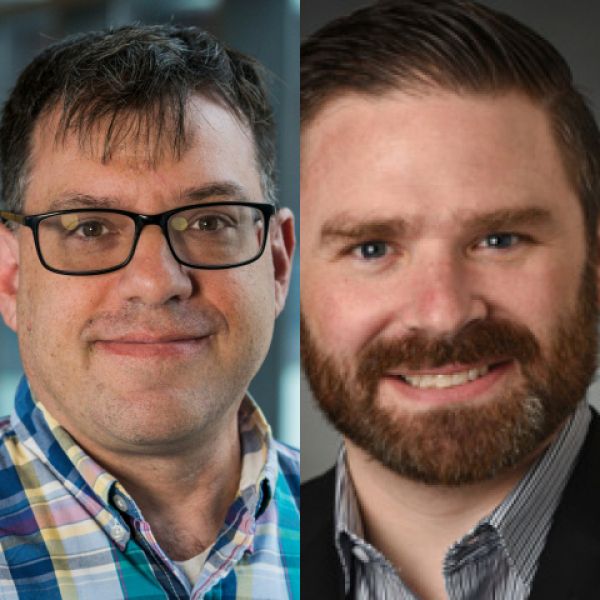
Huck-supported graduate degree programs transition to new leadership
David Koslicki and Greg Shearer have stepped into the leadership roles for the Huck's Bioinformatics and Genomics (BG) and Physiology graduate programs.
Full Article

Aug 29, 2023
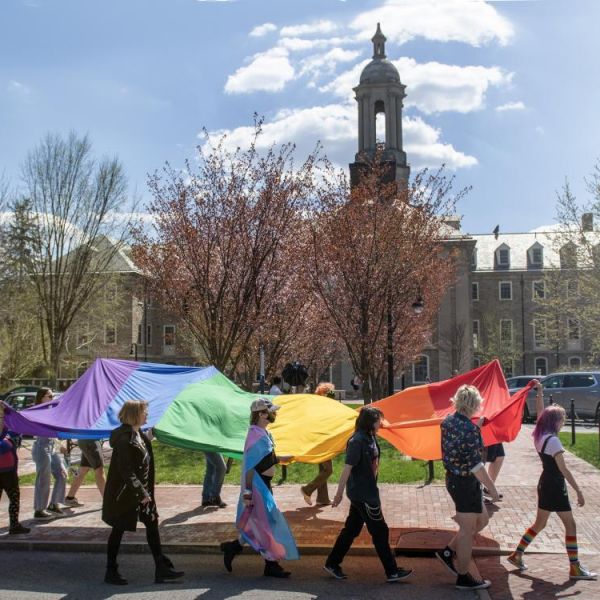
Penn State again named among nation's most LGBTQ-friendly universities
Penn State has once again earned a spot on Campus Pride’s “Best of the Best” LGBTQ-friendly College and Universities list, achieving an overall 5 out of 5 stars in the Campus Pride Index for 2023. Institutions are evaluated on eight LGBTQ-friendly factors, including housing, campus safety, academics, student life, and recruitment and retention efforts.
Full Article
Aug 24, 2023
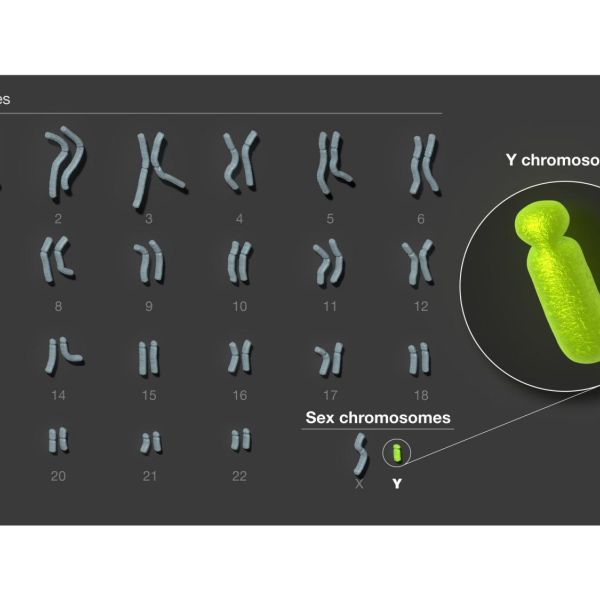
DNA sequence of the human Y chromosome fully determined for first time
The first full sequence of the last human chromosome — the Y chromosome — to be assembled is complete, thanks to an international collaboration that includes Penn State researchers. The new sequence, which fills in gaps across more than 50% of the Y chromosome’s length, uncovers genomic features with implications for fertility, as well as cancer risk and severity.
Full Article

Jul 26, 2023
HGSAC looks to raise the bar with election of new co-chairs
HGSAC students elected Avery Sicher and Jessica Walnut to serve as the graduate co-advisors to the Huck Institutes for the upcoming 2023-24 academic year.
Full Article

Apr 13, 2023
Penn State announces 2023 University-wide faculty and staff awards
Each spring, Penn State recognizes outstanding faculty and staff with annual awards in teaching and excellence. These awards highlight many of the University's faculty and staff who go above and beyond in their work at Penn State.
Full Article

Feb 17, 2023
Penn State biochemist Denise Okafor receives 2023 Marion Milligan Mason Award
C. Denise Okafor, assistant professor of biochemistry and molecular biology and of chemistry at Penn State, has been selected as a recipient of the 2023 Marion Milligan Mason Award for Women in the Chemical Sciences by the American Association for the Advancement of Science (AAAS).
Full Article

Dec 07, 2022
Many genes linked to alcohol and tobacco use are shared among diverse ancestries
Penn State researchers co-led a large genetic study that identified more than 2,300 genes predicting alcohol and tobacco use after analyzing data from more than 3.4 million people.
Full Article

Nov 30, 2022
Huck Grad Students Work Towards Inclusion
A discussion and advocacy group started by student leadership is pushing for dialogue and solutions to make the Huck a more welcoming and empowering space for scientists from all backgrounds.
Full Article
Nov 02, 2022
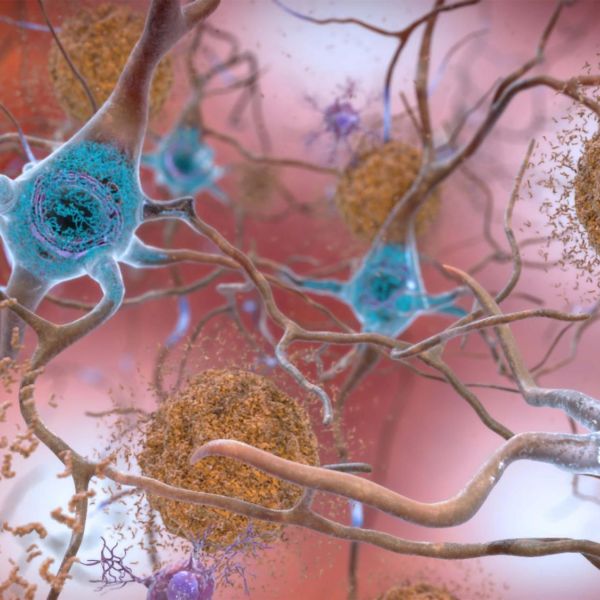
Two Alzheimer’s drugs tested head-to-head in first-ever virtual clinical trial
An estimated 6.2 million Americans ages 65+ are living with Alzheimer's disease. The national Alzheimer's Association predicts the number to grow to 13.8 million by 2060, barring the development of medical breakthroughs that would prevent, slow or cure the debilitating disease.
Full Article
Oct 19, 2022
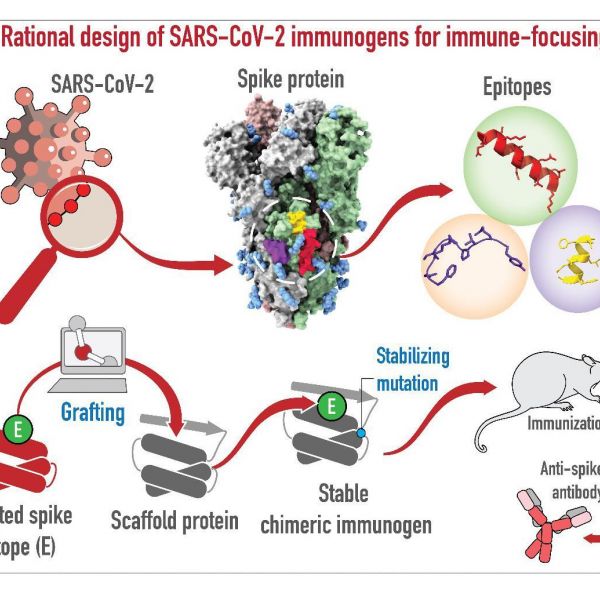
Newly engineered protein could be used to develop adaptation-proof COVID vaccine
A vaccine design approach that could protect against new variants of SARS-CoV-2 — the virus that causes COVID-19 — but also potentially protects against other coronaviruses is one step closer to reality as a result of research at Penn State College of Medicine.
Full Article