News

Apr 09, 2025
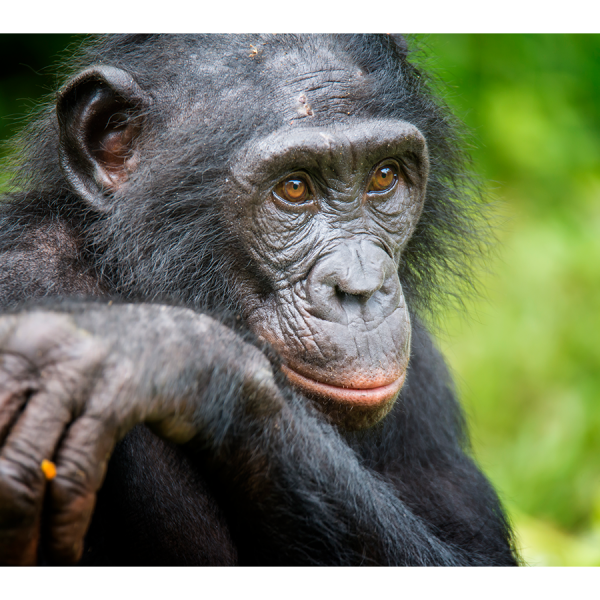
Complete genome sequences of six ape species unveiled
Differences among the DNA of seven ape species — including humans — are greater than originally thought, according to an international team led by researchers at Penn State, the National Human Genome Research Institute, and the University of Washington.
Full Article

Apr 09, 2025
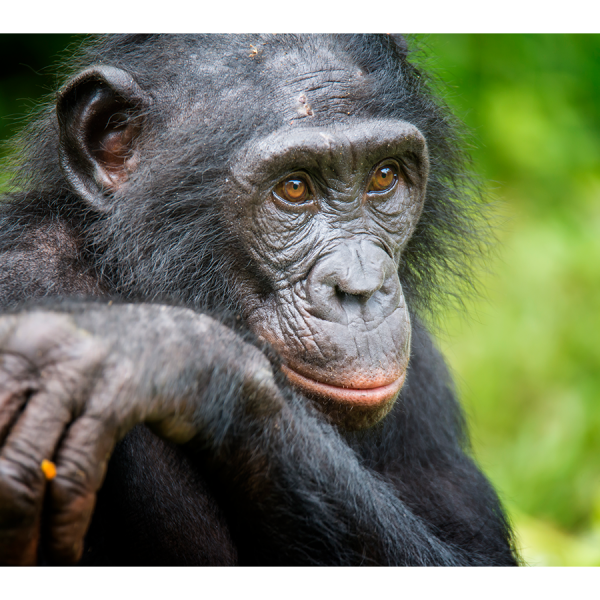
Complete genome sequences of six ape species unveiled
Previously inaccessible regions reveal novel insights that may advance understanding of evolution and conservation genetics for endangered apes as well as human health.
Full Article
Apr 09, 2025
NCEMS working groups to answer molecular and cellular bioscience questions
The U.S. National Science Foundation National Synthesis Center for Emergence in the Molecular and Cellular Sciences at Penn State aims to drive multidisciplinary collaboration utilizing publicly available research data.
Full Article

Mar 28, 2025
Four Penn State faculty elected AAAS Fellows
Four Penn State faculty members in areas ranging from agriculture to the biological sciences, geology and physics have been elected to the latest cohort of fellows of the American Association for the Advancement of Science (AAAS), the world’s largest general scientific society and publisher of the journal Science.
Full Article
Mar 26, 2025
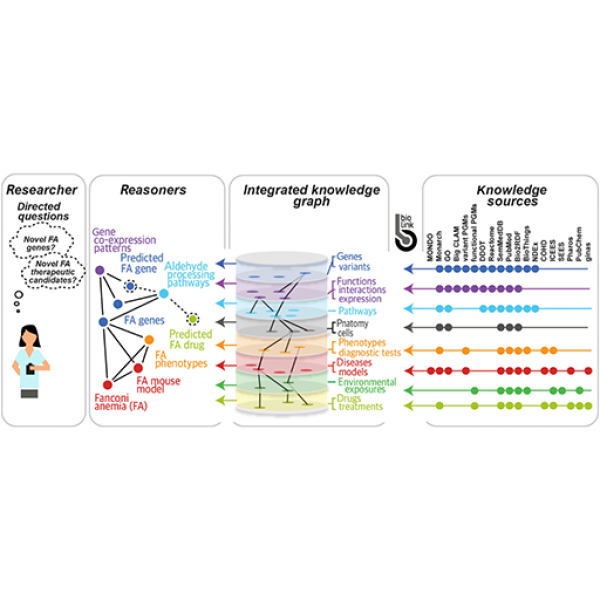
Translator for biomedical research aims to speed up patient care
$12.8M, five-year project brings together multiple institutions to improve and expand NIH Biomedical Data Translator
Full Article

Mar 18, 2025
BioArtist Mellissa Monsoon to present 'Collaborating with Microbes'
The One Health Microbiome Center and College of Arts and Architecture are co-hosting three events as part of a multi-year SciArt collaboration.
Full Article

Mar 17, 2025
Ag Sciences research institute SAFES funds projects addressing critical issues
Penn State’s College of Agricultural Sciences, through its Institute for Sustainable Agricultural, Food and Environmental Science, known as SAFES, announced funding awards to accelerate the advancement of its Critical Issues Initiatives. These initiatives serve as the college’s impact hubs, addressing urgent and high-impact challenges through targeted efforts and innovative projects.
Full Article

Mar 17, 2025
Virtual lecture to explore the importance of maintaining healthy ecosystems
On March 25, Erika Ganda, an assistant professor in Penn State’s Department of Animal Science, will discuss via Zoom how microbes in animals, people and the environment are interconnected through a concept known as “One Health.” The lecture is part of the Penn State Alumni Association's Virtual Speaker Series.
Full Article
Mar 17, 2025
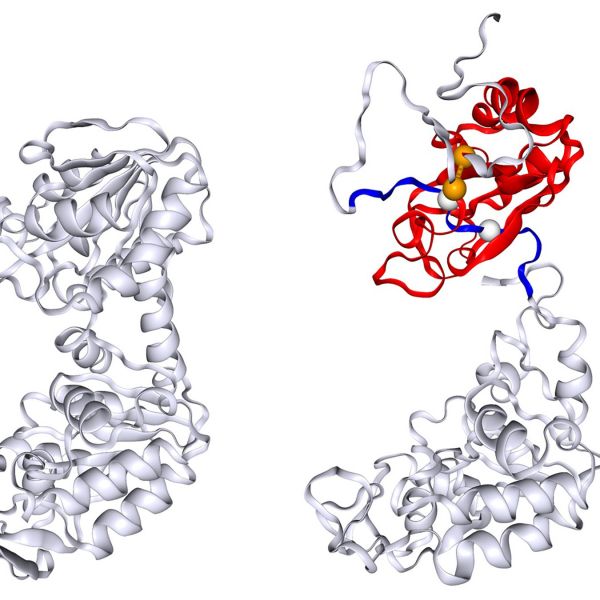
Protein accidentally lassos itself, helping explain unusual refolding behavior
New study demonstrates a potential protein misfolding mechanism that could solve a decades-old mystery of why some proteins refold in a different pattern than expected.
Full Article
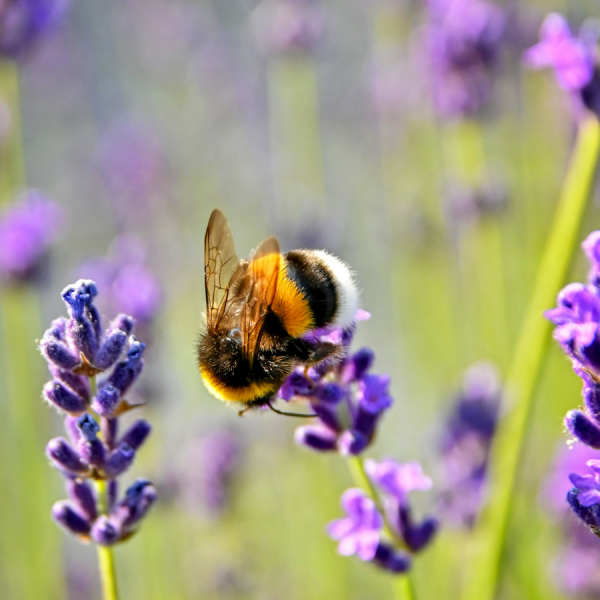

Mar 12, 2025
Analyzing genetic ‘signatures’ may give insight into what stresses wild bees
A new method of examining gene expression patterns called landscape transcriptomics may help pinpoint what causes bumble bees stress and could eventually give insight into why bee populations are declining overall.
Full Article